





No lab centers are available in this city
Max Lab
Jul 25, 2023
Gonorrhea - a topic that may make some uncomfortable, but one that deserves our attention. This sexually transmitted infection (STI) affects millions of people worldwide and can have serious health consequences if left untreated. In this blog post, we will dive deep into the world of gonorrhea, exploring its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment options available. Whether you're seeking information for yourself or simply curious about this prevalent STI, read on to discover everything you need to know about gonorrhea - from head to toe!
Gonorrhea, also known as "the clap," is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. This pesky bacterium primarily targets the moist and warm areas of the body, such as the reproductive tract, including the cervix, uterus, and fallopian tubes in women, and the urethra in both men and women. However, it can also infect other parts of the body like the rectum or throat through various sexual activities.
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the Neisseria gonorrhoeae bacterium. It can affect both men and women, and its symptoms may vary depending on the location of the infection.
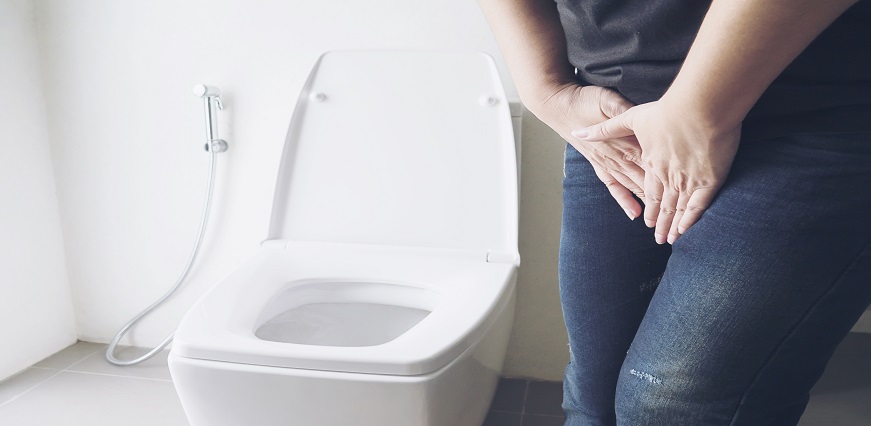
In men, common symptoms of gonorrhea include a burning sensation while urinating, increased frequency or urgency to urinate, and a white, yellow, or green discharge from the penis. Some men may also experience testicular pain or swelling.
Women with gonorrhea often have mild or no symptoms at all. However, when symptoms do occur, they typically include painful urination, increased vaginal discharge that may be yellowish or bloody, and pelvic pain.
Both men and women can develop throat infections if they engage in oral sex with an infected partner. In these cases, sore throat and swollen lymph nodes in the neck are common symptoms.
Rectal infections can occur in individuals who engage in anal intercourse. Symptoms may include rectal pain, itching or bleeding; discharge; and discomfort during bowel movements.
One of the main causes of Gonorrhea is engaging in unprotected sex with multiple partners or having sex with someone who has the infection. This includes both penetrative and non-penetrative sexual activities.
Another cause of Gonorrhea is not using barrier methods such as condoms during sexual intercourse. Condoms act as a protective barrier against the bacteria and can greatly reduce the risk of contracting the infection.
Additionally, having a history of previous sexually transmitted infections (STIs) can increase the likelihood of acquiring Gonorrhea. Infections such as chlamydia make individuals more susceptible to contracting other STIs, including Gonorrhea.
It's important to note that Gonorrhea can also be passed from mother to baby during childbirth if the mother has an active infection at that time.
Understanding and being aware of these causes can help individuals take necessary precautions to prevent contracting or spreading this sexually transmitted infection.
Detecting and diagnosing gonorrhea is crucial in order to begin treatment promptly and prevent the spread of the infection. If you suspect that you may have contracted gonorrhea, it's essential to seek medical attention as soon as possible.
When diagnosing gonorrhea, healthcare professionals typically start by asking about your symptoms and sexual history. They will inquire about any recent unprotected sexual encounters or potential exposure to someone with a known gonorrhea infection.
Next, they may perform a physical examination, which can include checking for any signs of inflammation or discharge from the genitals. In some cases, a swab test may be conducted by collecting samples from sites such as the urethra (in men) or cervix (in women). These samples are then sent to a laboratory for analysis.
Additionally, urine tests can also be used to diagnose gonorrhea. This method is especially common when there are no visible symptoms present but there is still suspicion of an infection.
It's important to note that if you engage in high-risk behaviors or have multiple sexual partners, regular screening for sexually transmitted infections including gonorrhea is recommended. Early detection through testing is key in preventing complications and ensuring prompt treatment.
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the Neisseria gonorrhoeae bacterium. If left untreated, it can lead to serious health complications. Fortunately, there are effective treatment options available.
The primary treatment for gonorrhea is antibiotics. The most commonly prescribed antibiotic is ceftriaxone, usually given as an injection in combination with oral azithromycin. This dual therapy helps ensure that the bacteria are fully eradicated from the body.
It's important to complete the full course of antibiotics as directed by your healthcare provider, even if symptoms improve before finishing the medication. This helps prevent antibiotic resistance and ensures that all traces of the infection are eliminated.
In addition to antibiotics, it's crucial to notify your sexual partners so they can also get tested and receive appropriate treatment if necessary. It's recommended to abstain from sexual activity until both you and your partner(s) have completed treatment and received clearance from a healthcare professional.
Prevention of Gonorrhea is crucial in order to avoid the transmission and spread of this sexually transmitted infection (STI). There are several steps that individuals can take to reduce their risk of contracting gonorrhea.
First and foremost, practicing safe sex is essential. This means using condoms consistently and correctly during every sexual encounter, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex. Condoms create a barrier that helps prevent the exchange of bodily fluids, reducing the chances of infection.
Furthermore, limiting sexual partners can also help lower the risk of gonorrhea. The more sexual partners an individual has, the higher their chances are of coming into contact with someone who may have the infection.
Regular testing for STIs is another important preventive measure. It is recommended that sexually active individuals get tested regularly for gonorrhea and other STIs, even if they do not have any symptoms. Early detection allows for prompt treatment and reduces the likelihood of transmission.
Open communication with sexual partners about STI status is also crucial in prevention efforts. Having honest conversations about past sexual history and exchanging information about recent test results can help make informed decisions regarding safer sex practices.
Gonorrhea is a common STI that can lead to severe health complications if not treated promptly. Recognizing its symptoms and seeking medical attention early on is crucial for effective treatment and preventing further spread of the infection.
Remember: knowledge about Gonorrhoea - Symptoms Causes Diagnosis & Treatment empowers you to take control over your sexual health!












Sign up takes less than 60 secs and gives you access to your offers, orders and lab tests.
Looks like you are not registered with us. Please Sign up to proceed
OTP will be sent to this number by SMS
We have successfully received your details. One of the agents will call you back soon.
 To reach our help desk call 9213188888
To reach our help desk call 9213188888
No Lab Centers are available in this city
Looks like you are not registered with us. Please Sign up to proceed
OTP will be sent to this number by SMS
Not Registered Yet? Signup now.Looks like you are not registered with us. Please Sign up to proceed





 7982100200
7982100200.png)
Comments