





No lab centers are available in this city

Max Lab
Nov 12, 2022
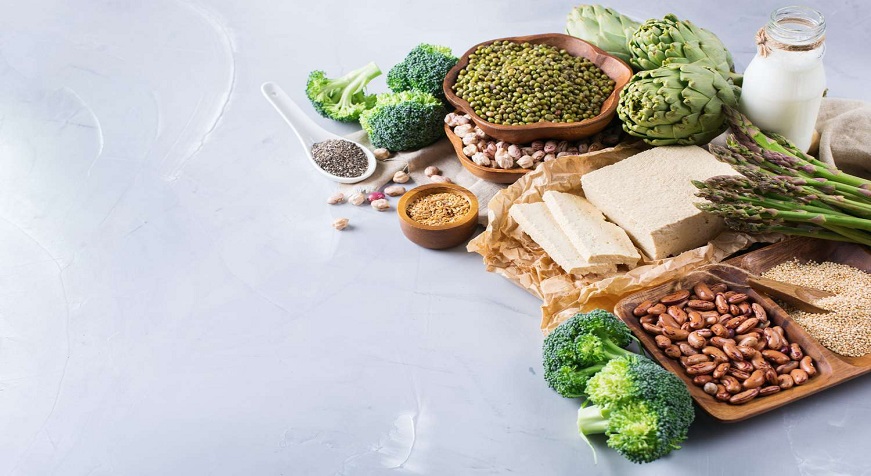
Protein is a crucial macronutrient that supports our bodies in cell growth and repair. It's especially important for athletes and bodybuilders to consume enough protein to help build muscle. However, getting enough protein doesn't have to mean eating meat all the time. There are plenty of delicious, protein-rich vegan foods that can help you reach your fitness goals. In this blog post, we'll share some of our favorite protein-rich vegan recipes that are sure to help you bulk up.
A vegan diet has many benefits. It can lower your risk of heart disease, help you lose weight, and reduce your risk of cancer.
Vegan diets are also associated with lower cholesterol levels, lower blood pressure, and a reduced risk of type 2 diabetes. Plus, they’re good for the environment.
When someone says they are vegetarian, it means that they do not eat meat. Some people choose to be vegetarian for ethical reasons, while others do so for health reasons. Either way, it is important to make sure that you are getting enough protein in your diet.
There are many high protein foods that vegetarians can eat to make sure they are getting enough protein. Here are some examples:
Seitan is a protein-rich vegan food that is made from wheat gluten. It is a popular meat alternative in many vegan and vegetarian diets. Seitan has a chewy, meaty texture and can be flavored in many different ways. It is an excellent source of protein and can be used in a variety of recipes.
Though not as popular as in recent years, Greek yogurt is still a great source of protein for vegetarians. It is made by straining yogurt to remove its whey, giving it a thicker consistency and a slightly sour taste. Greek yogurt typically has double the protein of regular yogurt, making it a filling and satisfying snack. Add some fruit or nuts for a complete meal or snack on its own.
Lentils are an excellent source of protein, providing 18 grams of protein per cooked cup. They're also a good source of fiber and complex carbohydrates, making them a satisfying and nutritious food. Lentils can be used in a variety of recipes, including soups, stews, salads, and veggie burgers.
Chia seeds are an excellent source of protein for vegetarians and vegans. A single ounce (28 grams) of chia seeds contains 4 grams of protein, which is about as much as a small egg.
In addition to being a good source of protein, chia seeds are also high in fiber and omega-3 fatty acids. They have been shown to improve blood sugar control, reduce inflammation, and promote heart health.
If you're looking for a way to add more protein to your diet, consider adding chia seeds to your meals and snacks. You can add them to smoothies, sprinkle them on top of yogurt or oatmeal, or use them in baking.
Quinoa is a protein-rich grain that can be used in place of rice or other grains. It is a good source of fiber and minerals, and it is gluten-free. Quinoa can be cooked in many different ways, and it can be served as a side dish or main course.
For vegans, cottage cheese is a fantastic source of protein. It is high in calcium and low in fat, making it a healthy option for those looking to add more protein to their diets. Cottage cheese can be used in a variety of recipes, or simply eaten as a snack.
Hemp seeds are a complete protein, meaning they contain all 20 amino acids that the body needs to function properly. Just one ounce (28 grams) of hemp seeds provides 10 grams of protein — as much as an egg!
But that’s not all. Hemp seeds are also a rich source of omega-3 fatty acids, which are important for maintaining heart health and preventing chronic diseases like diabetes and cancer.
Beans are an excellent source of protein and contain all the essential amino acids your body needs to build and maintain muscle tissue. A single cup of cooked beans provides around 15 grams of protein, making them a great addition to any meal or snack. Additionally low in fat and cholesterol, beans are a healthy food.
Edamame is a popular protein-rich veg food. It is a type of soybean that is often eaten as a snack or used as an ingredient in various dishes. Edamame is high in protein, fiber, and vitamins, and low in calories and fat. This makes it an excellent choice for those looking to add more protein to their diet without increasing their calorie intake.
Green peas are a great source of protein, with each serving providing around 9 grams. They're also a good source of fiber, vitamins C and K, manganese, and folate. Plus, they're low in calories and fat. Add them to soups, salads, pasta dishes, or simply enjoy them as a side dish. However you eat them, you'll be getting a good dose of protein and other nutrients.
Peanut butter is a popular food made from roasted peanuts. It is high in protein and fat, and has a distinctive flavor and texture. Peanut butter is an excellent source of protein, and can be a healthy part of a balanced diet. It can be used as a spread on bread or crackers, or as an ingredient in recipes. Peanut butter is a good choice for people who are looking for a high-protein, nutritious food.
Almonds are a protein-rich nut that contains all 20 amino acids, making it a complete protein. Just a quarter-cup of almonds contains 6 grams of protein, making them an excellent addition to any meal or snack. Almonds are also packed with healthy fats, fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Almonds are a heart-healthy food that can help lower cholesterol and improve blood sugar control.
When it comes to protein-rich veg foods, eggs are one of the best options out there. Eggs are packed with high-quality protein, and they're also a good source of other nutrients like vitamin D and choline. Additionally, they can be utilised in a wide range of recipes due to their extreme versatility.
There are many factors that contribute to how much protein an adult needs, including activity level, weight, and muscle mass. For an average adult, the Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) for protein is 56 grammes per day, or 0.36 grammes per pound of body weight. However, athletes and other active adults may need more protein, while sedentary adults may need less.
Protein requirements also increase with age. This is because older adults tend to have less muscle mass and a higher risk of sarcopenia, a condition characterized by muscle wasting. As such, the RDA for adults over the age of 50 is 0.45-0.55 grams per pound of body weight, or about 68-82 grams per day.
It's important to note that these are just general guidelines and that your individual needs may vary depending on your unique circumstances. If you're unsure about how much protein you need, speak to a registered dietitian or certified nutritionist who can help you create a personalized plan.
The protein requirements for women are different than those for men, so it’s important to know how much protein you need to stay healthy. The recommended daily allowance (RDA) for protein is 46 grams per day for women. However, this number increases if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
Protein is an important nutrient that helps your body build and repair tissue, produce enzymes and hormones, and boost immunity. It’s also essential for keeping your hair and nails healthy.
If you’re not getting enough protein from your diet, you may be at risk for developing various health problems, such as weak bones, anemia, and muscle wasting.
Protein is an essential nutrient for children, as it helps to build and repair tissues, produce hormones and enzymes, and boost immunity. The amount of protein required depends on a child's age, activity level, and overall health.
The recommended dietary allowance (RDA) for protein is 0.36 grams per pound (0.8 grams per kg) of body weight. For example, a child who weighs 50 pounds (23 kg) would need 18 grams of protein per day.
Active children and teens may need more protein than the RDA to support their growth and development. Some experts recommend 1 to 1.2 grams of protein per pound (2.5 to 3 grams per kg) of body weight for active kids.
Certain health conditions may also require a higher-protein diet. For example, children with celiac disease or other gastrointestinal disorders may need more protein to help offset any malnutrition that can occur due to their condition.
A variety of foods can provide the proteins kids need, including meat, poultry, fish, beans, lentils, nuts, seeds, eggs, and dairy products like milk and yogurt. Protein-rich plant foods are especially important for vegetarian and vegan kids to make sure they're getting all the nutrients they need.
Also Read:











Sign up takes less than 60 secs and gives you access to your offers, orders and lab tests.
Looks like you are not registered with us. Please Sign up to proceed
OTP will be sent to this number by SMS
We have successfully received your details. One of the agents will call you back soon.
 To reach our help desk call 9213188888
To reach our help desk call 9213188888
No Lab Centers are available in this city
Looks like you are not registered with us. Please Sign up to proceed
OTP will be sent to this number by SMS
Not Registered Yet? Signup now.Looks like you are not registered with us. Please Sign up to proceed





 7982100200
7982100200.png)
Comments