

Home > Category > Infectious Disease Test > Infectious Disease Test in Rudrapur
Showing 1 - 15 of 47
Diagnosing the reason for an infection can sometimes feel like detective work. Infectious disease diagnostics in Rudrapur, a critical component of medicine, involves using various tests to identify the specific microorganism responsible for making you feel sick.
Infectious disease tests in Rudrapur, also called diagnostic tests for infectious disease or infectious disease diagnostic tests, are a diverse group of medical procedures designed to detect the cause of an infection. Blood tests for infectious diseases are a common type, but depending on the suspected infection, other samples like urine, stool, or a swab from the throat or nose can be collected. These tests can be widely classified into two main approaches:
1. Direct detection of the pathogen: This type of test aims to identify the specific microorganism causing the infection. This could involve techniques like culturing the bacteria or virus in a laboratory setting, detecting the organism's genetic material (DNA or RNA), or identifying the organism itself via microscopic examination.
2. Indirect detection of the immune response: This type of test looks for evidence of the body's immune system response to the infection. This could involve measuring the levels of antibodies, proteins produced by the immune system in response to a particular pathogen.
The specific test will depend on several factors, including the type of symptoms you're experiencing, the suspected cause of the infection, and your doctor's clinical judgment.
There are several scenarios in which a doctor might recommend an infectious disease test in Rudrapur. Here are some common examples:
The time required to obtain the results of an infectious disease test can vary depending on the type of test performed. Laboratory tests such as bacterial cultures may take several days, while rapid tests may provide results within minutes or hours. The cost and turnaround time of infectious disease tests can also vary depending on your location and the specific lab performing the test in Rudrapur.
Once the test results are available, your doctor will discuss them with you and determine the best course of treatment. This may involve antibiotics for bacterial infections, antiviral medications for viral infections, or other treatments depending on the specific diagnosis.
An infectious disease is a health disorder caused by pathogens, like parasites, bacteria, viruses, and fungi, that enter the body. Usually, infectious diseases are contagious, spreading from one person to another through bug bites or contaminated food or water.
The symptoms of infectious diseases vary, depending on the illness. For example, fungal infections may cause localised symptoms, like itching or rash. In contrast, viral and bacterial infections may cause symptoms in many areas of the body, including chills, fever, cough, congestion, gastrointestinal issues, fatigue, muscle aches, and headache.
There are a variety of pathogens that can invade the body from the outside and cause infectious diseases. These include parasites, bacteria, viruses, fungi, and prions. Symptoms may develop when the pathogens start damaging or destroying the cells of the body and as the immune system responds to the presence of the infection.
There are several simple measures that can be taken to reduce the risk of developing infections and even to prevent certain illnesses. Vaccination is a good way of avoiding many types of infectious diseases, like chickenpox, hepatitis A and B, HPV, COVID-19, diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, influenza, malaria, tuberculosis, etc. Other measures include ensuring safe food handling, maintaining proper hygiene, covering the nose and mouth when coughing or sneezing, avoiding contact with people who have an infection, not drinking or swimming in contaminated water, avoiding unprotected sex, etc.
Infectious diseases may affect anyone. However, a weakened immune system or frequent travel to areas with high instances of infectious diseases can increase one’s risk of developing an infection. Younger children, people over the age of 60, pregnant women, unvaccinated individuals, and healthcare workers are also at a higher risk of contracting infectious diseases.
Many types of infectious diseases can be cured, depending on what causes the infection. Bacterial infections are generally treated with antibiotics, while most viral infections can be managed with over-the-counter medication to alleviate symptoms. Fungal infections can be cured by using antifungal medication, and infections caused by parasites can be cured by anti-parasitic drugs.

Diphtheria may not be a term you hear every day, but understanding this infec...Read More

The world is constantly keeping an eye on emerging viruses, and the latest on...Read More

Have you ever experienced an itchy, uncomfortable sensation in your ear that ...Read More
Diabetic foot ulcers are a serious concern for those living with diabetes. Th...Read More

Norovirus is a term that many people have heard but may not fully understand....Read More

As the seasons change, many of us look forward to blooming flowers and warmer...Read More

Malaria is more than just a disease; it's a formidable adversary that can...Read More

As the leaves begin to change and a crispness fills the air, many of us start...Read More

Rat Bite Fever might sound like a scenario from a horror movie, but it's ...Read More
Bacterial infections are more common than you might think, lurking behind eve...Read More

Yellow fever is a term that often evokes concern and curiosity. This viral di...Read More
The Human body is one of the most complicated machines and to ensure that it ...Read More

Also referred to as snail fever, schistosomiasis is a disease caused by paras...Read More
Strongyloidiasis is an infection caused by the parasitic worm Strongyloides. ...Read More
Understanding the Cryptococcus Fungus Cryptococc...Read More

Getting bitten by a mosquito is quite common, however, a mosquito bite can tu...Read More

For many people, a mosquito bite is nothing more than just a nuisance. It gen...Read More
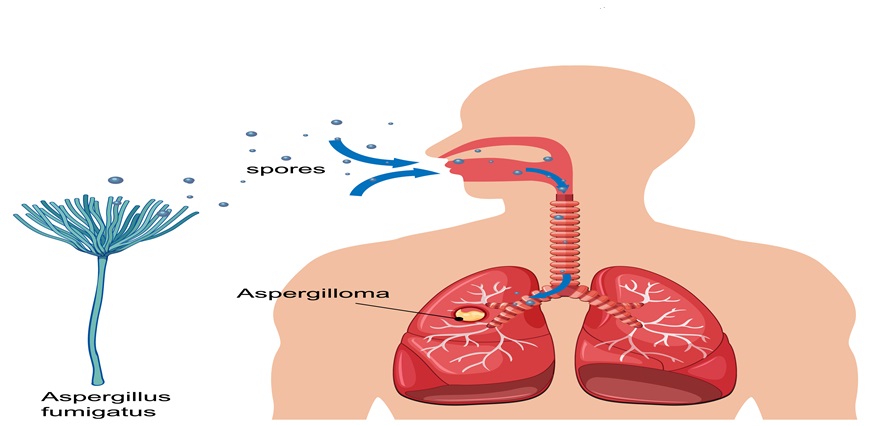
Aspergillosis is a fungal infection caused by Aspergillus, a...Read More

Rocky Mountain spotted fever (RMSF) is a bacterial illness caused by Ricketts...Read More

Hyperpigmentation is a common skin condition where patches o...Read More
Mumps viral disease is most known for causing puffy cheeks f...Read More
The Nipah Virus, or NIV, is a zoonotic disease that primarily spreads from fr...Read More

Chagas disease, also known as American trypanosomiasis, is a...Read More

Meningitis is an infection and inflammation of the fluids and membranes surro...Read More
Hepatitis is a medical condition that is commonly caused by ...Read More

Purpura refers to discoloured patches on the skin or mucous ...Read More

For those dealing with mysterious, persistent allergies, an Immunoglobulin E ...Read More

Air pollution poses major health risks and can exacerbate respiratory disease...Read More

When it comes to our health, knowledge truly is power. And when faced with sy...Read More

Welcome to our blog post on lower respiratory infections - a topic that affec...Read More

Bacterial infections can be a pain to deal with, and sometimes waiting for me...Read More

Are you feeling unwell and unsure of the cause? A torch test may be what you ...Read More

Are you feeling unwell and not sure what's causing it? Have you ever hear...Read More
Have you ever heard of an ANA test? It's a simple blood test that can hel...Read More

Are you familiar with Hepatitis C? It is a viral infection that affects the l...Read More
Are you experiencing itchy, red, or scaly skin? It might be more than just a ...Read More

Are you concerned about the H1N1 influenza virus and its potential impact on ...Read More
Have you ever wondered why your doctor asks for a urine culture test? You mig...Read More
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are a serious concern in today's wor...Read More
Do you experience persistent fatigue, inflammation, or joint pain? If so, an ...Read More

Eczema (or dermatitis) is a general term for inflammation of the skin. Dermat...Read More

Chickenpox is a highly contagious virus that usually infects children under t...Read More

Did you know that waterborne diseases can cause about 90% of all diarrhoea il...Read More

Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are infections of the urinary system that are...Read More
Selenium is an essential component of various enzymes and proteins called sel...Read More

The digestive canal of an individual is susceptible to various kinds of infec...Read More