





No lab centers are available in this city
Max Lab
Jul 11, 2024
Mumps viral disease is most known for causing puffy cheeks from swollen salivary glands. While fever, fatigue, and muscle aches come first, the signature swelling arrives later. There’s no cure, but rest, pain relievers, and hydration help. The MMR vaccine is the best defence against mumps virus symptoms and its complications like deafness or testicular inflammation.
Most cases of mumps occur in children between the ages of two and twelve. This is because their immune systems haven’t fully developed and they haven’t likely received the full course of vaccinations yet. However, you can also detect mumps virus in adults if they haven’t been previously infected or vaccinated. The virus is highly contagious and spreads through close contact with infected saliva. This can happen by coughing, sneezing, sharing utensils, or even kissing someone who has mumps.
Mumps Virus
The main cause of mumps virus belongs to a family of viruses called paramyxoviruses. Unlike some other viruses, it specifically targets the salivary glands, it triggers an immune response, causing them to swell and become painful. This inflammation is the reason behind the characteristic puffy cheeks associated with mumps. The mumps viral disease is highly contagious and spreads through contact with infected saliva. Once it enters your body, the virus travels to the salivary glands, particularly the parotid glands located near your ears. Here, the virus replicates rapidly, triggering your immune system to attack.
The mumps viral infection can spread from an infected person’s nose, throat or mouth if they sneeze, cough or talk. Mumps caused by coming in close contact with an infected person attacks people with weak immune system or who aren’t vaccinated against the virus.
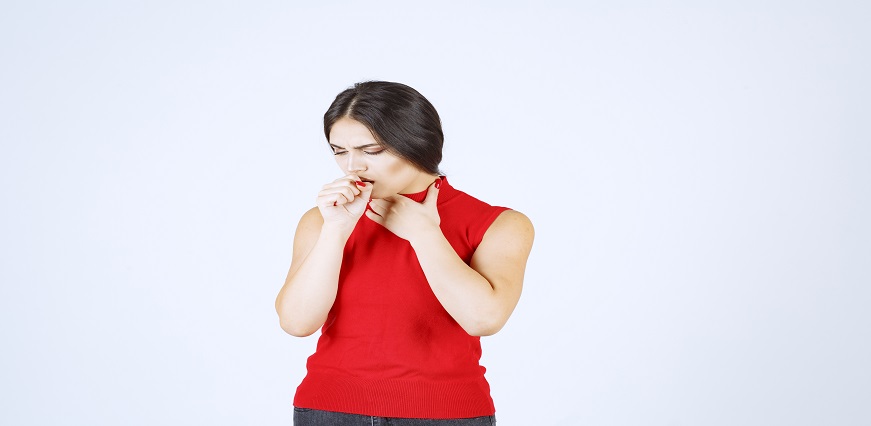
Mumps viral disease can strike at any age, but the symptoms may vary slightly between children and adults.
In Children:
In Adults:
Prevention
Mumps viral disease, caused by the mumps virus, is a highly contagious illness that can cause puffy cheeks, fever, and fatigue. Thankfully, there’s a powerful tool available to prevent this infection.
The MMR (measles, mumps, rubella virus) vaccine is the best defence against mumps virus prevention. This combination vaccine protects against three distinct, yet related, viruses: measles, mumps, and rubella. All three viruses spread through contact with infected saliva or respiratory droplets and can cause serious complications.
Two doses of the MMR vaccination are usually administered. The first dosage is given to the child between the ages of 12 and 15 months, and the second dose is given to the child between the ages of 4 and 6. This two-dose schedule offers optimal protection against mumps and other vaccine-preventable diseases.
Prior to the introduction of the MMR vaccine in 1967, mumps viral disease was a common childhood illness. However, widespread vaccination has significantly reduced mumps cases. This not only protects individuals but also helps achieve herd immunity, making it harder for the virus to spread in the community.
Here’s a breakdown of the MMR vaccine and its role in mumps virus prevention:
By getting vaccinated with MMR, you're not just protecting yourself against mumps virus symptoms but also safeguarding against the potential complications of measles and rubella.
Remember, vaccination is the most effective way to prevent mumps viral disease and its complications. Talk to your doctor to ensure you and your family are properly vaccinated against mumps and other preventable illnesses.
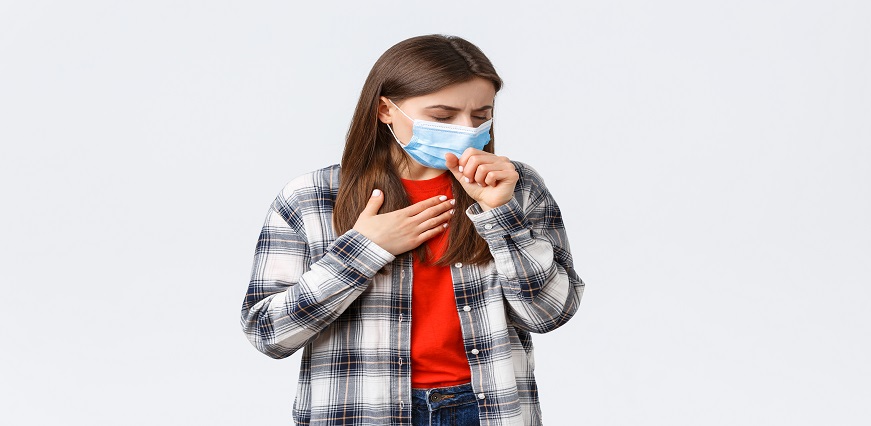
Unfortunately, there's no specific mumps viral treatment that directly targets the virus itself. Mumps is a viral infection, and antibiotics, which fight bacterial infections, have no effect on it. However, there are steps you can take to manage the symptoms and promote a faster recovery:
















Sign up takes less than 60 secs and gives you access to your offers, orders and lab tests.
Looks like you are not registered with us. Please Sign up to proceed
OTP will be sent to this number by SMS
We have successfully received your details. One of the agents will call you back soon.
 To reach our help desk call 9213188888
To reach our help desk call 9213188888
No Lab Centers are available in this city
Looks like you are not registered with us. Please Sign up to proceed
OTP will be sent to this number by SMS
Not Registered Yet? Signup now.Looks like you are not registered with us. Please Sign up to proceed





 7982100200
7982100200.png)
Comments