





No lab centers are available in this city
Max Lab
Jul 26, 2023
By measuring the levels of PSA in your blood, doctors can detect any abnormalities and determine if further investigation or treatment is necessary.
It's important to note that elevated levels of PSA don't always indicate cancer. Various factors such as age, inflammation, infection, or even certain medical procedures can cause fluctuations in these levels. That's why it's crucial not to jump to conclusions based solely on a high result from the PSA test.
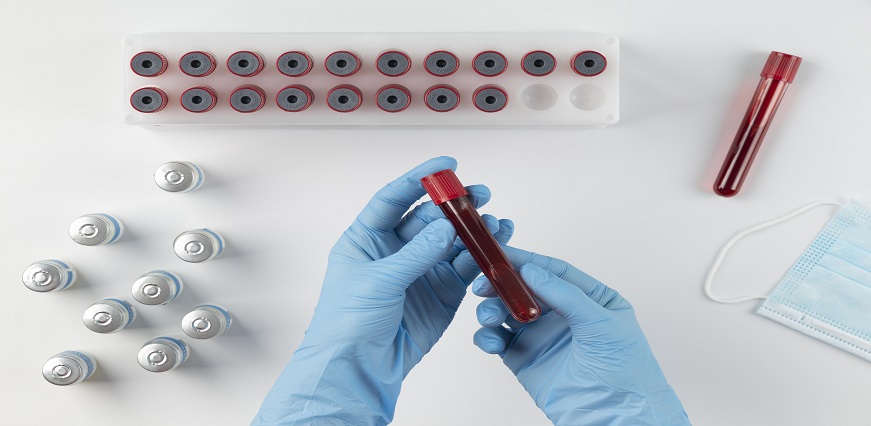
To administer this simple yet significant screening tool, all you need is a small sample of blood taken from your arm. This sample then undergoes laboratory analysis where technicians measure and assess the level of PSA present.
The purpose of the PSA test is to measure the levels of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) in a man's blood. PSA is a protein produced by both cancerous and non-cancerous cells in the prostate gland. The test helps doctors evaluate the health of the prostate and screen for potential problems, such as prostate cancer.
One of the main purposes of the PSA test is to detect early signs of prostate cancer. Elevated levels of PSA may indicate that there is an abnormality in the prostate, which could be due to cancer or other conditions like prostatitis or benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). By monitoring changes in PSA levels over time, doctors can identify any significant increases that may warrant further investigation.
Additionally, the PSA test can also be used to monitor patients who have already been diagnosed with prostate cancer. It helps track their response to treatment and detect any recurrence or progression of the disease.
High levels of PSA may indicate the presence of prostate cancer. However, it's important to note that other factors can also cause an increase in PSA levels. For example, benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), which is non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland, can lead to elevated PSA readings. Inflammation and infection within the prostate can also cause temporary spikes in PSA levels.
On the other hand, low levels of PSA are typically considered normal and healthy. It suggests that there are no major issues with the prostate gland at present. However, it's important to remember that every individual is unique and what constitutes "normal" may vary from person to person.
When interpreting PSA test results, healthcare professionals take into account various factors including age and overall health status before making any conclusions about potential abnormalities or risks associated with high or low levels.
For men who are at average risk of developing prostate cancer, guidelines recommend starting PSA testing at age 50. However, for individuals with a higher risk, such as African American men or those with a family history of prostate cancer, screening may begin earlier around age 45. It's best to consult with your healthcare provider to determine the appropriate timing based on your individual circumstances.
The interval between subsequent tests also depends on the initial level of PSA detected. If your levels are found to be within normal range and you have no other risk factors, retesting every two years is generally recommended. However, if there is an elevated or abnormal result in your first test or if you have additional risk factors, more frequent testing might be necessary.
It's essential to discuss with your doctor about the right timing and frequency for future PSA screenings based on your unique situation. Remember that regular monitoring plays a crucial role in detecting any changes early and effectively managing potential risks associated with prostate health.
One potential risk is that elevated levels of PSA can indicate the presence of prostate cancer when there may not actually be any. This is known as a false positive result. False positives can lead to unnecessary anxiety and further invasive procedures such as biopsies, which carry their own set of risks including infection and bleeding.
Conversely, there's also the risk of false negatives - where low levels of PSA are detected even though prostate cancer is present. This can provide a false sense of security, delaying necessary treatment and potentially allowing the cancer to progress.
It's also worth noting that age plays a role in determining appropriate screening guidelines for PSA testing. Older men may have higher baseline levels of PSA due to benign enlargement or inflammation in the prostate gland, leading to more frequent false positives.
Additionally, overdiagnosis is another concern associated with routine PSA testing. Some prostate cancers are slow-growing and may never cause symptoms or affect lifespan; however, detecting them through routine screening could lead to unnecessary treatment with its own potential side effects such as impotence and urinary incontinence.
While the PSA test serves an important purpose in detecting potential cases of prostate cancer early on, it's essential to consider both its benefits and limitations. Understanding the risks involved can help individuals make informed decisions about whether or not they should undergo this test.











Sign up takes less than 60 secs and gives you access to your offers, orders and lab tests.
Looks like you are not registered with us. Please Sign up to proceed
OTP will be sent to this number by SMS
We have successfully received your details. One of the agents will call you back soon.
 To reach our help desk call 9213188888
To reach our help desk call 9213188888
No Lab Centers are available in this city
Looks like you are not registered with us. Please Sign up to proceed
OTP will be sent to this number by SMS
Not Registered Yet? Signup now.Looks like you are not registered with us. Please Sign up to proceed





 7982100200
7982100200.png)
Comments