





No lab centers are available in this city
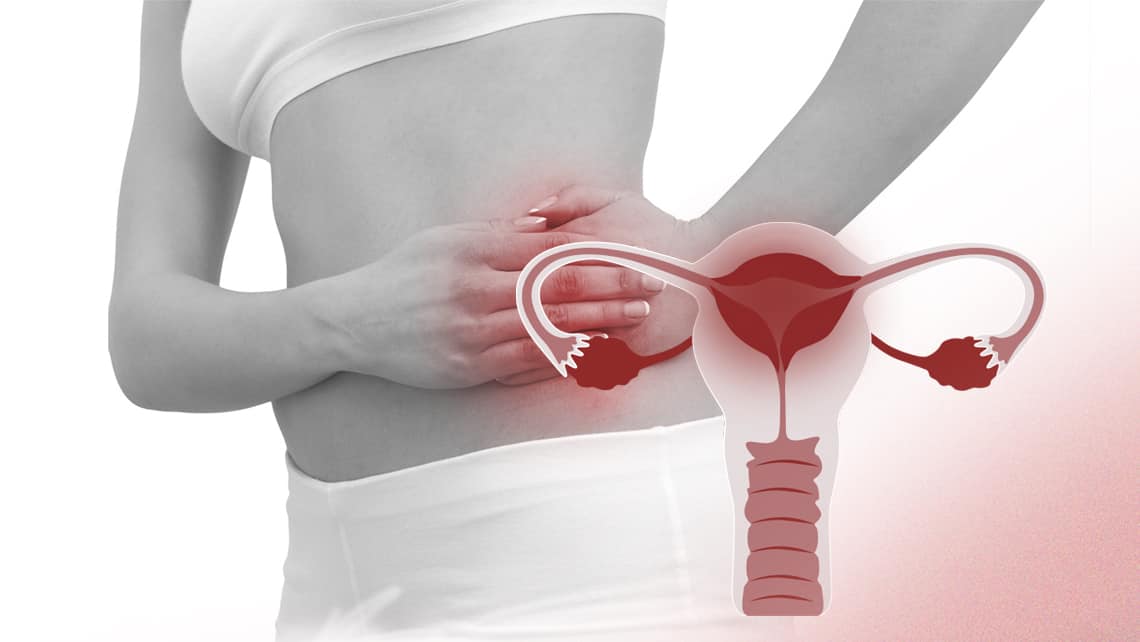
An infection of a woman's reproductive organs is known as a Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID). It's usually caused by a sexually transmitted infection that enters the body during sexual contact. PID symptoms are usually pain in the lower abdomen and vaginal discharge. Prompt PID treatment, usually antibiotics, helps ease discomfort and avoid complications like infertility. Your partner should get tested too!
Pelvic inflammatory disease, or PID, is a serious infection that affects the female reproductive system. PID can make it difficult or impossible to get pregnant and can be deadly if not treated right away.
Reproductive organs that can be affected by PID include the uterus, ovaries and fallopian tubes. When you have PID, you may experience pain in your lower abdomen (belly). You might also notice unusual discharge (leaking) from your vagina.
15% of Pelvic Inflammatory Disease are not sexually transmitted, although unprotected intercourse is still the main way that most people contract Pelvic Inflammatory Disease. During sexual activity, bacteria may enter the reproductive system and infect the organs.
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease can harm your uterus, ovaries, and fallopian tubes, as well as other reproductive organs. Pelvic Inflammatory Disease can cause discomfort and make future pregnancies challenging. A tubo-ovarian abscess (TOA), which can cause serious illness if left untreated, is another complication of Pelvic Inflammatory Disease.
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) affects more than a million India women annually. In addition, it renders over 100,000 women sterile, preventing them from getting pregnant. Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) can also lead to ectopic pregnancies in several circumstances. Ectopic pregnancy refers to when the baby starts to develop outside the uterus, most usually in the fallopian tube. Untreated ectopic pregnancy necessitates immediate medical attention.
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) cases have decreased recently. The primary infections that cause Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID), chlamydia and gonorrhea, are being routinely tested for by more women, which may be the cause.
If you have gonorrhoea, chlamydia, or have ever had a STI, your chance of developing Pelvic Inflammatory Disease increases. Pelvic Inflammatory Disease, however, can occur even if you have never had a STI.
Additional elements that may increase your risk of Pelvic Inflammatory Disease include:
Symptoms of Pelvic Inflammatory Disease are absent in some female patients. Women who do experience symptoms may experience the following:
Pain from Pelvic Inflammatory Disease may be minimal to moderate. However, some women experience extreme discomfort and symptoms, including:
Call your doctor right away if you have severe symptoms, or visit the emergency department. Your bloodstream or other areas of your body may now be infected. This may endanger your life.
Visit your healthcare practitioner as soon as possible if you get Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) symptoms. Your chances of receiving successful therapy increase the sooner you seek it.
Your healthcare provider can typically identify Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) by:
Tests might I need to diagnose Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
Your provider may also order:
In some cases, your provider may recommend:
Culdocentesis involves inserting a needle behind the vagina to extract fluid for analysis. Although considerably less common now than it formerly was, this surgery can be beneficial on occasion.
To treat Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID), your doctor probably wants you to take antibiotics. Your doctor might prescribe you two different types of antibiotics to treat a variety of germs as they may not be able to identify the specific bacteria that caused your infection.
Your symptoms may become better or disappear a few days after starting medication. Even if you feel better, you still need to finish your medication. If you stop taking your medicine too soon, the infection can come back.
Your doctor can refer you to the hospital for treatment if you are ill or pregnant, have trouble swallowing pills, or develop an abscess (a pocket of pus brought on by an infection) in your pelvic.
Inflammatory illness of the pelvis might call for surgery. This is a rare situation that should only be undertaken if an abscess in your pelvis ruptures or if your doctor has reason to believe that it will. If the infection doesn't respond to treatment, it can also be required.
Sexual contact can spread the germs that cause Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID). If you engage in sexual activity, your partner should also receive Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) treatment. Men may covertly harbour the bacteria that cause pelvic inflammatory disease.
If your partner doesn't get medical attention, your infection can come back. You could be told to forgo sexual activity until the infection has been treated.
Sometimes a sexually transmitted infection is not the cause of Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID). After ordinary vaginal bacteria enter your reproductive organs, it could start there. Douching needs to be avoided in order to lower the risk.
However, unprotected intercourse is the primary cause of Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) most of the time. Take action to engage in safe sex. Take the following precautions to avoid STIs that can lead to Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID).
If you suspect Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID), schedule a medical appointment. A UTI, for example, might mimic Pelvic Inflammatory Disease in symptoms. Your doctor can perform a Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) test and rule out other problems, though.
If you don't get treatment for your Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID), your symptoms could get worse and cause issues like:
The infection may also spread to different body areas. It may endanger your life if it spreads to your blood.
Antibiotics can treat Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) if you receive quick diagnosis and treatment for an infection. However, treatment won't be able to undo any harm that has already been done to your reproductive organs. Don't put off getting help. Visit your doctor right soon to receive the care you require to maintain your health.
 Allergy Test
Allergy Test
 Anemia Test
Anemia Test
 Auto immune
Auto immune
 Blood disorder
Blood disorder
 Bone and Joint
Bone and Joint
 Cancer Test
Cancer Test
 Cardiology Test
Cardiology Test
 Covid Recovery
Covid Recovery
 Dengue Test
Dengue Test
 Depression
Depression
 Diabetes Test
Diabetes Test
 Fatigue
Fatigue
 Fever Test
Fever Test
 Full body
Full body
 Gastro Test
Gastro Test
 Gastrointestinal
Gastrointestinal
 Gynaecology Test
Gynaecology Test
 Heart Test
Heart Test
 HIV Test
HIV Test
 Hormone Test
Hormone Test
 Hypertension
Hypertension
 Immunity Test
Immunity Test
 Infectious Disease
Infectious Disease
 Infertility Test
Infertility Test
 Influenza Test
Influenza Test
 Iron Test
Iron Test
 Kidney Test
Kidney Test
 Liver Test
Liver Test
 Lung Test
Lung Test
 Nephrology
Nephrology
 Obesity
Obesity
 Orthopedics Test
Orthopedics Test
 Physician
Physician
 Pollution Health Checkup
Pollution Health Checkup
 Pregnancy Test
Pregnancy Test
 Prostate Test
Prostate Test
 Senior Citizen Test
Senior Citizen Test
 STD Test
STD Test
 Thyroid Test
Thyroid Test
 Tuberculosis Test
Tuberculosis Test
 Vitamin Test
Vitamin Test
 Women Health Test
Women Health Test
Sign up takes less than 60 secs and gives you access to your offers, orders and lab tests.
Looks like you are not registered with us. Please Sign up to proceed
OTP will be sent to this number by SMS
We have successfully received your details. One of the agents will call you back soon.
 To reach our help desk call 9213188888
To reach our help desk call 9213188888
No Lab Centers are available in this city
Looks like you are not registered with us. Please Sign up to proceed
OTP will be sent to this number by SMS
Not Registered Yet? Signup now.Looks like you are not registered with us. Please Sign up to proceed





 7982100200
7982100200.png)