





No lab centers are available in this city

Max Lab
Nov 06, 2022
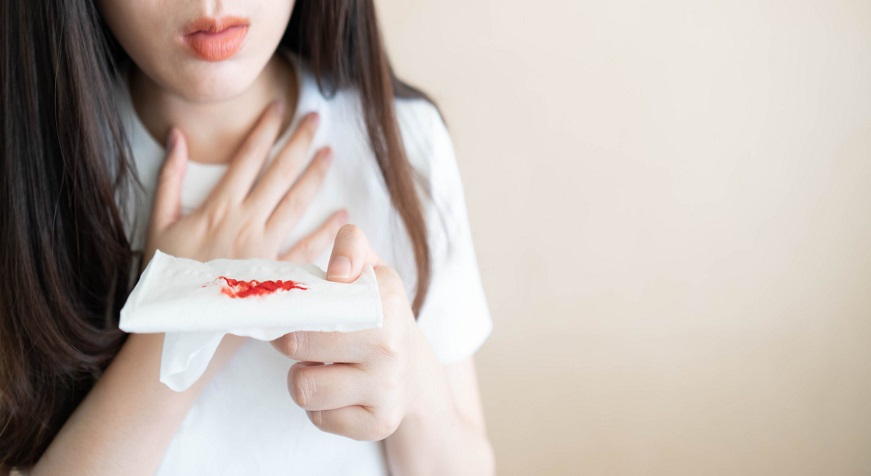
Coughing up blood can be a sign of a serious medical condition, such as lung cancer or tuberculosis. It can also be a symptom of less serious conditions, such as bronchitis. If you cough up blood, it is important to see a doctor so that the cause can be diagnosed and treated. This blog post will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for coughing up blood.
When you cough up blood, it's called hemoptysis. It can be frightening, but fortunately, it's usually not a sign of something serious. Most often, coughing up blood is a result of an infection or a bronchial obstruction. In rare cases, it could be a sign of lung cancer.
If you're coughing up small amounts of blood, it's likely not cause for concern. However, if you're coughing up larger amounts of blood, or if you have other symptoms like shortness of breath or chest pain, you should see a doctor right away. Diagnosing the cause of hemoptysis can be tricky, so your doctor will likely order a number of tests, including a chest X-ray and a CT scan. Once the cause is determined, treatment can begin. If your hemoptysis is caused by an infection, antibiotics may be prescribed. If it's due to a bronchial obstruction, your doctor may recommend surgery to remove the obstruction. In rare cases where lung cancer is the cause, treatment will depend on the type and stage of the cancer.
While coughing is a normal and healthy bodily function, there are times when it can be a sign of something more serious. Blood in cough, also called hemoptysis, is a symptom that merits medical attention.
Blood in a cough can be caused by a number of things, ranging from minor to serious. For example, nosebleeds or blood vessels bursting in the respiratory tract due to coughing can both lead to blood in a cough. However, blood in a cough can also be indicative of more serious conditions like tuberculosis, lung cancer, or pulmonary embolism.
If you are coughing up blood, it is important to seek medical attention right away. Your doctor will likely order some tests to determine the cause of your hemoptysis. Treatment for blood in cough will depend on the underlying cause but may include antibiotics, surgery, or radiation therapy.
When you have blood in your cough, it is called hemoptysis. Many different things can cause this, but the most common causes are bronchitis and lung cancer.
Other possible causes of hemoptysis include tuberculosis, pneumonia, pulmonary embolism, and congestive heart failure. In rare cases, blood in the cough can be caused by a tear in the blood vessels in the lungs (known as a pulmonary hemorrhage).
If you are coughing up blood, it is important to see a doctor right away so that the cause can be determined and treated appropriately.
Bronchiectasis is a condition in which the airways of the lungs become damaged and widened. This leads to a buildup of mucus, which can make it difficult to breathe. Bronchiectasis often occurs as a result of another lung disease, such as cystic fibrosis or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It can also be caused by an infection, such as pneumonia. Symptoms of bronchiectasis include:
- A persistent cough that produces mucus
- Shortness of breath
- Wheezing
- Chest pain
- Fatigue
- Repeated infections of the lungs
If you have bronchiectasis, it is important to see your doctor regularly. Treatment typically involves antibiotics to clear respiratory infections, bronchodilators to open up the airways, and Pulmonary Rehabilitation. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove damaged parts of the lungs.
Acute bronchitis is a condition in which the airways in your lungs become inflamed. This can lead to a buildup of mucus, which can cause coughing and difficulty breathing. The common cold or the flu are two viral infections that frequently lead to bronchitis. It might occasionally be brought on by a bacterial infection.
The bacteria Mycobacterium tuberculosis is the source of the infection known as tuberculosis (TB). It most commonly affects the lungs and can cause coughing up blood. Other symptoms of TB include chest pain, fatigue, weight loss, and fever. If left untreated, TB can be fatal.
TB is diagnosed through a combination of a physical exam, chest x-ray, and skin test. A skin test is done by injecting a small amount of solution into the skin on the arm. If the person is infected with TB, a hard bump will develop at the injection site within 48 hours.
TB is treated with a combination of antibiotics taken for several months. It is important to finish the entire course of medication even if you are feeling better. Stopping treatment early can allow TB to become resistant to antibiotics, which makes it much harder to treat.
When you have cancer, the abnormal cells in your body divide and grow out of control. A cough is a common symptom of cancer, but it can also be caused by other conditions. If you have a cough that doesn’t go away, it’s important to see your doctor so they can figure out the cause.
There are many different types of cancer, and each one can cause a different type of cough. For example, lung cancer can cause a productive cough, which means you might coughing up blood or phlegm. Other types of cancer, such as throat cancer, can cause a dry cough.
Coughing is usually just one symptom of cancer. Other common symptoms include fatigue, weight loss, and pain. If you have any of these symptoms, it’s important to see your doctor so they can check for cancer.
If your doctor suspects you have cancer, they will order tests to confirm the diagnosis. These tests might include a chest x-ray, CT scan, or biopsy. Once your doctor has diagnosed your cancer, they will develop a treatment plan to help you fight the disease.
A fungal infection is a common cause of blood in cough. The most common type of fungal infection is candidiasis, which is caused by the yeast Candida albicans. Candida is a normal part of the human body's microflora, but it can overgrow and cause an infection. Other types of fungal infections include aspergillosis, histoplasmosis, and cryptococcosis.
Symptoms of fungal infection can vary depending on the type of infection. Candidiasis typically causes white patches on the throat or tongue, soreness, and redness. Aspergillosis can cause coughing up blood, shortness of breath, wheezing, and chest pain. Histoplasmosis can cause fever, chills, chest pain, and coughing up blood. Cryptococcosis can cause fever, headache, malaise, and coughing up blood.
A diagnosis of a fungal infection is typically made based on symptoms and laboratory testing. Treatment for a fungal infection generally includes antifungal medication.
Blood in cough can be a sign of a serious condition, so it is important to seek medical attention if your child is coughing up blood. The main causes of blood in cough are:
-A ruptured blood vessel: this can happen due to coughing too hard or from an infection.
-A bronchial infection: this is usually caused by bacteria or viruses and can result in inflammation and bleeding.
-A lung tumor: while this is rare, it is a possible cause of coughing up blood.
-Coughing up bloody mucus or phlegm
-Rusty-colored or bright red blood in the saliva or mucus
-Difficulty breathing
-Wheezing or a high-pitched noise when breathing (stridor)
If your child has any of these symptoms, it is important to see a doctor right away as they could be indicative of a serious condition. The doctor will likely order a chest x-ray and/or CT scan to look for the source of the bleeding. Treatment will depend on the underlying cause but may include antibiotics, inhaled steroids, or surgery.
Coughing up blood during pregnancy can be a sign of a serious medical condition. If you are coughing up blood, it is important to seek medical attention immediately.
There are several possible causes of coughing up blood during pregnancy. One possibility is that it is a symptom of preeclampsia. Preeclampsia is a condition that can occur during pregnancy, and it is characterized by high blood pressure and protein in the urine. Preeclampsia can cause major issues for the mother and the unborn child if it is not managed.
Another possibility is that coughing up blood is a sign of placenta previa. When the placenta completely or partially covers the cervix, it is called placenta previa. This can be a very serious condition, as it can cause bleeding during pregnancy. If you have placenta previa, you will need to be monitored closely by your healthcare provider.
Yet another possibility is that coughing up blood is a sign of pulmonary embolism. Pulmonary embolism occurs when there is a blockage in one of the arteries leading to the lungs. This can be a life-threatening condition, so it is important to seek medical attention immediately if you think you may have this condition.
If you are coughing up blood during pregnancy, it is important to seek medical attention right away. Your healthcare provider will likely order some tests to determine the cause of your bleeding. Treatment will depend on the underlying cause of
A diagnosis of blood in cough can be a challenge for both the patient and health care provider. There are many potential causes of this symptom, which can range from benign to life-threatening. A thorough history and physical examination are crucial in making the correct diagnosis.
In some cases, diagnostic testing may be necessary to confirm the cause of blood in cough. This may include ordering a chest x-ray, sputum culture, or blood tests. In more severe cases, a bronchoscopy or lung biopsy may be needed.
Treatment for blood in cough will vary depending on the underlying cause. In many cases, no treatment is necessary and the symptom will resolve on its own. However, more serious conditions may require medication or surgery.
If you have blood in your cough, it is important to see a doctor right away. Blood in cough can be a symptom of a serious underlying condition, such as lung cancer or tuberculosis. Treatment for blood in cough will depend on the underlying cause. If you have lung cancer, treatment may involve surgery, radiation therapy, or chemotherapy. If you have tuberculosis, treatment will usually involve taking antibiotics for several months.
Prevention for blood in cough may include:
- limiting exposure to secondhand smoke and smoking
- avoiding exposure to environmental and occupational irritants, such as fumes, dust, and chemicals
- managing underlying health conditions that may contribute to coughing up blood, such as heartburn, GERD, asthma, and emphysema
- taking medications as prescribed to help manage conditions that may cause coughing up blood
- drinking plenty of fluids to keep the throat lubricated and prevent irritation
- maintaining regular brushing and flossing as part of healthy oral hygiene
If you cough up blood, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. This is because coughing up blood can be a sign of a serious medical condition, such as lung cancer or a pulmonary embolism.
If blood is coming up in your cough, you should:
-Call your doctor or go to the emergency room right away
-Avoid smoking and exposure to secondhand smoke
-Avoid drinking alcohol
-Limit your activity level and get plenty of rest
-Drink lots of fluids (preferably water) to stay hydrated
-Use a humidifier to thin the mucus in your lungs and make it easier to cough up
-Try over-the-counter (OTC) medicines, such as guaifenesin or bronchodilators, to help relieve your symptoms
Coughing up blood can be a sign of a serious medical condition, so it is important to seek medical attention if you experience this symptom. Blood in cough can be caused by a variety of conditions, including infections, lung cancer, and other respiratory diseases. A doctor will need to evaluate your symptoms and perform tests to determine the cause of your cough and any potential underlying health problems. Treatment for blood in cough will vary depending on the underlying cause, but may include antibiotics, surgery, or other therapies.
When you cough up blood, it's called hemoptysis. It can be frightening, but fortunately, it's usually not a sign of something serious. Most often, coughing up blood is a result of an infection or a bronchial obstruction.
Symptoms of blood in a cough include :
When you have blood in your cough, it is called hemoptysis. Many different things can cause this, but the most common causes are bronchitis and lung cancer.Other possible causes of hemoptysis include tuberculosis, pneumonia, and congestive heart failure.
If blood is coming up in your cough, you should:
There are several possible causes of coughing up blood during pregnancy. One possibility is that it is a symptom of preeclampsia. Preeclampsia is a condition that can occur during pregnancy, and it is characterized by high blood pressure and protein in the urine.
This may include ordering a
In more severe cases, a bronchoscopy or lung biopsy may be needed.
Treatment for blood in the cough will depend on the underlying cause like treatment may involve surgery, radiation therapy, or chemotherapy. Sometimes you have to take antibiotics for several months.











Sign up takes less than 60 secs and gives you access to your offers, orders and lab tests.
Looks like you are not registered with us. Please Sign up to proceed
OTP will be sent to this number by SMS
We have successfully received your details. One of the agents will call you back soon.
 To reach our help desk call 9213188888
To reach our help desk call 9213188888
No Lab Centers are available in this city
Looks like you are not registered with us. Please Sign up to proceed
OTP will be sent to this number by SMS
Not Registered Yet? Signup now.Looks like you are not registered with us. Please Sign up to proceed





 7982100200
7982100200.png)
Comments